Google Inc. (GOOG) stands as perhaps the most renowned name in the tech world as well as among US stocks, showcasing robust revenue and earnings growth amid challenging macroeconomic conditions.
However, beneath the surface, questions loom about the long-term sustainability of its search business revenues in the face of advancing generative AI.
Despite commendable recovery and growth rates, investor sentiment remains cautious, casting shadows on Google stock’s deserved acknowledgment.
Notably, the company’s cloud division grapples with slower growth compared to Microsoft (MSFT), sparking speculations of market share loss, potentially influenced by MSFT’s alliance with OpenAI.
Today, we embark on a journey to decode the intricate numbers defining Google stock performance in 2023.
As we delve into the highs and lows, one thing remains steadfast: Google stock is not slowing down any time soon.
In the wider sea of stock options for the coming year, Google stock emerges as a stellar choice, its value echoing louder than the current market skepticism.
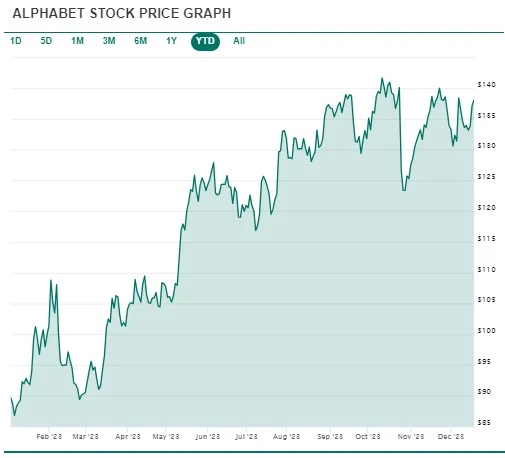
Google’s YTD Stock Chart
In 2023, Google stock embarked on a notable trajectory, marked by robust fundamental performance and a resilient market presence.
Despite distancing itself from the lows of the previous year, the stock’s valuation appears conservative, possibly underrating its quality.
In the third quarter, GOOGL showcased an 11% YoY revenue surge, reaching $76.7 billion, coupled with a commendable 300 bps expansion in operating margin, reaching 28%.
Diluted EPS grew by 46% YoY to $1.55, with a 30.6% YoY growth to $1.62 when excluding non-cash gains and losses. The Google Cloud segment reported a formidable 22% YoY growth, though overshadowed by MSFT’s stellar results.
A pivotal move involved reallocating costs tied to Google Research and DeepMind, impacting operating losses. Google Services experienced a rebound in growth rates at YouTube and Google Search, countering concerns about Bing’s competition.
GOOGL ended the quarter with $119.9 billion in cash, $30.9 billion in non-marketable securities, and $13.8 billion in debt.
Noteworthy was the company’s commitment to shareholder value, evident in a $15.8 billion stock repurchase alongside $22.6 billion in free cash flow.
Management highlighted the success of Shorts, Google’s answer to TikTok, averaging over 70 billion daily views.
Despite concerns about expense growth in 2024, the market may be overlooking Google’s competitive prowess, particularly in generative AI, where over 60% of major companies are clients.
Investors, however, remain cautious, questioning management’s commitment to sustained profitability amid exciting developments in loss-generating segments like Waymo’s autonomous driving unit.
The year 2023, with its financial intricacies, underscores the need for investors to consider both short-term challenges and long-term potentials in evaluating Google’s stock performance.
Exceptional Business Approach
Unlike CEOs engaging in unconventional challenges, Google’s management focuses on results rather than drama.
The company faces antitrust scrutiny but remains notably less controversial. A quiet comment section on Google articles signals a lack of sensationalism, reflecting the steadiness investors seek.
With YouTube flourishing and search revenue holding firm, Google proves resilient amid market fluctuations.
The recent drop in post-Q3 earnings seems more a result of speculative fervor than genuine concerns. Operating income has climbed by 10%, underscoring the company’s consistent growth.
Despite uncertainties in the market, Google’s 19.9x earnings valuation positions it favorably among Big Tech.
The fear of obsolescence is unwarranted, given Google’s strengthening network effects and formidable moat. Investors should note the choice between Class A (GOOGL) and Class C (GOOG) stock, with the former offering a better value.
AI Developments
In 2023, Google stock stands at a pivotal juncture in the AI landscape amidst the recent upheaval at OpenAI. As the leading player in AI, OpenAI faced internal turmoil, resulting in the departure of key figures like Sam Altman and Greg Brockman to Microsoft.
This development, while potentially advantageous for Microsoft, could create challenges for OpenAI’s team dynamics and productivity.
Conversely, Google’s approach with Bard, its ChatGPT competitor, has been steadfast and corporate from the start. With a strategic response to ChatGPT, Bard has steadily improved, incorporating Google’s extensive network features.
Notably, Bard remains a free product, positioning it favorably against ChatGPT. Google’s commitment is further evident in the accelerated pace of Bard updates, suggesting a dedicated effort to establish it as a premier chatbot and general AI product.
As OpenAI grapples with internal disruptions, Google’s Bard has quietly advanced in quality and functionality. Google’s decision to offer Bard for free, coupled with plans for an integrated fact-checking system and potential plugin ecosystem, strengthens its position.
This calculated progress, contrasting with OpenAI’s recent setbacks, positions Google as the potential long-term beneficiary of the AI landscape.
